In this tutorial, you'll find out how the bucket sort algorithm works. additionally, you'll find functional samples of bucket sorting by compartment in C, C ++, Java, and Python.
Bucket Sort may be a sorting technique that sorts items by first dividing the things into several groups called buckets. Items inside each bucket are sorted using one among the acceptable sorting algorithms or by recursively calling an equivalent algorithm.
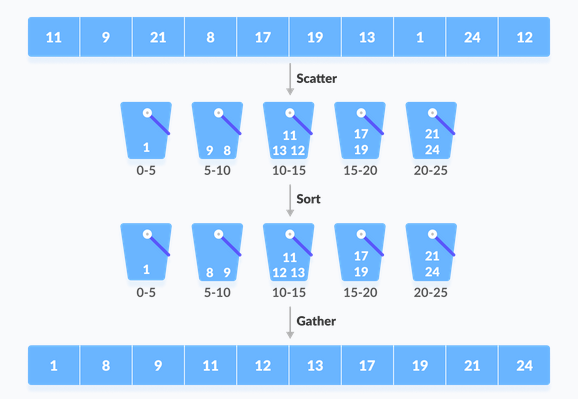
Several buckets are created. Each bucket is crammed with a selected range of things. Items inside the bucket are sorted using the other algorithm. Finally, the weather of the bucket is gathered to urge the sorted array.
The bucket sorting process is often understood as a dispersal approach. the things are first dispersed in buckets then the things within the buckets are sorted. Finally, the weather is put together so as.
Create an array of size 10. Each location during this array is employed as a bucket to store items.
Likewise, .25 is additionally inserted within the same bucket. Each time, the ground value of the floating-point number is taken.
If we take whole numbers as input, we'd like to divide it by the interval (10 here) to urge the ground value.
Likewise, other items are inserted into their respective buckets.
This makes the complexity of the algorithm wont to sort the things within the bucket depend.
The complexity gets even worse when the weather are in reverse order. If insertion sort is employed to sort the things within the bucket, the time complexity becomes O (n2).
The complexity becomes even better if the things inside the buckets are already sorted.
If insert sort is employed to sort items during a bucket, the general complexity at the best is going to be linear, ie. O (n + k). O (n) is that the complexity for creating the buckets and O (k) is that the complexity for sorting the weather of the bucket using algorithms with linear time complexity at the best.
Bucket sort program in c programming
Bucket Sort may be a sorting technique that sorts items by first dividing the things into several groups called buckets. Items inside each bucket are sorted using one among the acceptable sorting algorithms or by recursively calling an equivalent algorithm.
Several buckets are created. Each bucket is crammed with a selected range of things. Items inside the bucket are sorted using the other algorithm. Finally, the weather of the bucket is gathered to urge the sorted array.
The bucket sorting process is often understood as a dispersal approach. the things are first dispersed in buckets then the things within the buckets are sorted. Finally, the weather is put together so as.
How does the Bucket Sort Algorithm work?
- Suppose the input array is:
 |
| Bucket Sort Algorithm |
Create an array of size 10. Each location during this array is employed as a bucket to store items.
 |
| algorithm for bucket sort |
- Insert items into buckets from the array. the weather are inserted consistent with the reach of the bucket.
 |
| Bucket sort |
- In our code example, we've compartments each of which matches from 0 to 1, 1 to 2, 2 to 3, ...... (n-1) to n.
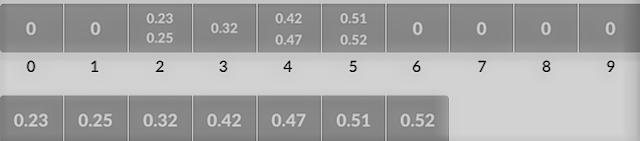
- Suppose an input element of .23 is taken. it's multiplied by the dimensions = 10 (i.e. .23 * 10 = 2.3). Then, it's converted to an integer (i.e. 2.3≈2). Finally, .23 is inserted into bucket-2.
Likewise, .25 is additionally inserted within the same bucket. Each time, the ground value of the floating-point number is taken.
If we take whole numbers as input, we'd like to divide it by the interval (10 here) to urge the ground value.
Likewise, other items are inserted into their respective buckets.
 |
| sorting algorithms |
- Items in each compartment are sorted using one among the stable sorting algorithms. Here we've used quicksort (built-in function).
 |
| bucket sort in c |
- The elements of every bucket are put together.
 |
| bucket sort algorithm |
bucket sort complexity
- Worst-case complexity: O (n2)
This makes the complexity of the algorithm wont to sort the things within the bucket depend.
The complexity gets even worse when the weather are in reverse order. If insertion sort is employed to sort the things within the bucket, the time complexity becomes O (n2).
- Best case complexity: O (n + k)
The complexity becomes even better if the things inside the buckets are already sorted.
If insert sort is employed to sort items during a bucket, the general complexity at the best is going to be linear, ie. O (n + k). O (n) is that the complexity for creating the buckets and O (k) is that the complexity for sorting the weather of the bucket using algorithms with linear time complexity at the best.
- Average complexity of cases: O (n)
Bucket Sort Algorithm
 |
| Bucket Sort Algorithm |
Bucket sort program in c programming
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h> #define NARRAY 7 #define NBUCKET 6 #define INTERVAL 10 struct Node { int data; struct Node *next; }; void BucketSort(int arr[]); struct Node *InsertionSort(struct Node *list); void print(int arr[]); void printBuckets(struct Node *list); int getBucketIndex(int value); // Sorting function void BucketSort(int arr[]) { int i, j; struct Node **buckets; // Create buckets and allocate memory size buckets = (struct Node **)malloc(sizeof(struct Node *) * NBUCKET); // Initialize empty buckets for (i = 0; i < NBUCKET; ++i) { buckets[i] = NULL; } // Fill the buckets with respective elements for (i = 0; i < NARRAY; ++i) { struct Node *current; int pos = getBucketIndex(arr[i]); current = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); current->data = arr[i]; current->next = buckets[pos]; buckets[pos] = current; } // Print the buckets along with their elements for (i = 0; i < NBUCKET; i++) { printf("Bucket[%d]: ", i); printBuckets(buckets[i]); printf("\n"); } // Sort the elements of each bucket for (i = 0; i < NBUCKET; ++i) { buckets[i] = InsertionSort(buckets[i]); } printf("-------------\n"); printf("Bucktets after sorting\n"); for (i = 0; i < NBUCKET; i++) { printf("Bucket[%d]: ", i); printBuckets(buckets[i]); printf("\n"); } // Put sorted elements on arr for (j = 0, i = 0; i < NBUCKET; ++i) { struct Node *node; node = buckets[i]; while (node) { arr[j++] = node->data; node = node->next; } } return; } // Function to sort the elements of each bucket struct Node *InsertionSort(struct Node *list) { struct Node *k, *nodeList; if (list == 0 || list->next == 0) { return list; } nodeList = list; k = list->next; nodeList->next = 0; while (k != 0) { struct Node *ptr; if (nodeList->data > k->data) { struct Node *tmp; tmp = k; k = k->next; tmp->next = nodeList; nodeList = tmp; continue; } for (ptr = nodeList; ptr->next != 0; ptr = ptr->next) { if (ptr->next->data > k->data) break; } if (ptr->next != 0) { struct Node *tmp; tmp = k; k = k->next; tmp->next = ptr->next; ptr->next = tmp; continue; } else { ptr->next = k; k = k->next; ptr->next->next = 0; continue; } } return nodeList; } int getBucketIndex(int value) { return value / INTERVAL; } void print(int ar[]) { int i; for (i = 0; i < NARRAY; ++i) { printf("%d ", ar[i]); } printf("\n"); } // Print buckets void printBuckets(struct Node *list) { struct Node *cur = list; while (cur) { printf("%d ", cur->data); cur = cur->next; } } // Driver code int main(void) { int array[NARRAY] = {42, 32, 33, 52, 37, 47, 51}; printf("Initial array: "); print(array); printf("-------------\n"); BucketSort(array); printf("-------------\n"); printf("Sorted array: "); print(array); return 0; }
Applications For the Bucket sort Algorithm
- the entry is evenly distributed over a variety.
there are floating-point values